Agglomerator
Previous
Next
- Agglomeration separation technology is a way of oil-water separation, also known as coarse-grained separation method, the use of the nature of the material (surface properties, fiber structure), the dispersed phase of the small droplets from small to large, under the action of gravity and other driving forces, so that the dispersed phase from the continuous phase of the removal of a technology, mainly including liquid-liquid agglomeration, gas-liquid agglomeration.
- Dispersed phase fluids are always mixed in the process flow and difficult to remove, and directly for the enterprise from production to operation of all aspects of the safety of potential hazards. Liquid-liquid agglomeration is a technology that removes dispersed-phase fluids from liquid fluids. In recent years, the separation of non-homogeneous liquid/liquid fluids has received special attention in the petroleum and chemical industries, and is an indispensable key unit for process security, equipment protection, fluid purification, finished fluid recovery and purification.
- The agglomerator is a multi-stage system; it first removes particulate matter and then agglomerates and separates the dispersed phase liquid from the continuous phase liquid.
Working Principle Of Agglomerator
- Stage 1: Pre-filtration
Due to the fine pore structure of the agglomerating media, it is recommended that a pre-filter be installed upstream of the agglomerator to remove most of the particulate matter from the liquid stream and to protect the agglomerating filter in a safe and efficient manner. - Stage 2: Agglomeration
A mixture of hydrocarbons and water enters the agglomerating element and flows from the inside to the outside. As the liquid passes through the specially designed agglomeration layer, the flow rate is greatly reduced and the tiny droplets in the dispersed phase combine and gather together in the agglomeration layer to form large liquid particles called agglomerates. - Stage 3: Separation
In the separation of water from fuel, anhydrous fuel and large water droplets flow towards the separation cartridge located in the same vertical vessel. The flow direction is from outside to inside. The separation cartridge is hydrophobic and prevents water from entering the cartridge. Only anhydrous fuel flows through the separation cartridge. In separating oil from water, the settling zone is designed to be downstream of the agglomerator. In the settling zone, large agglomerated droplets are separated by gravity.
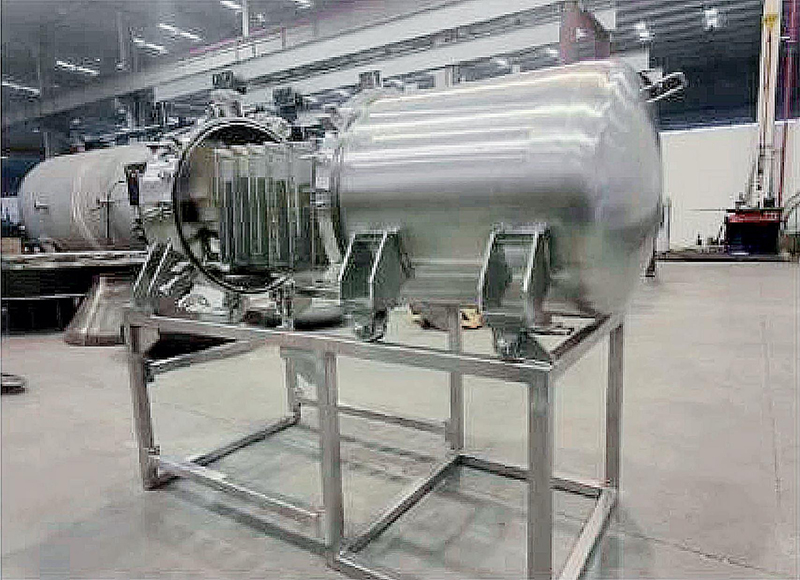
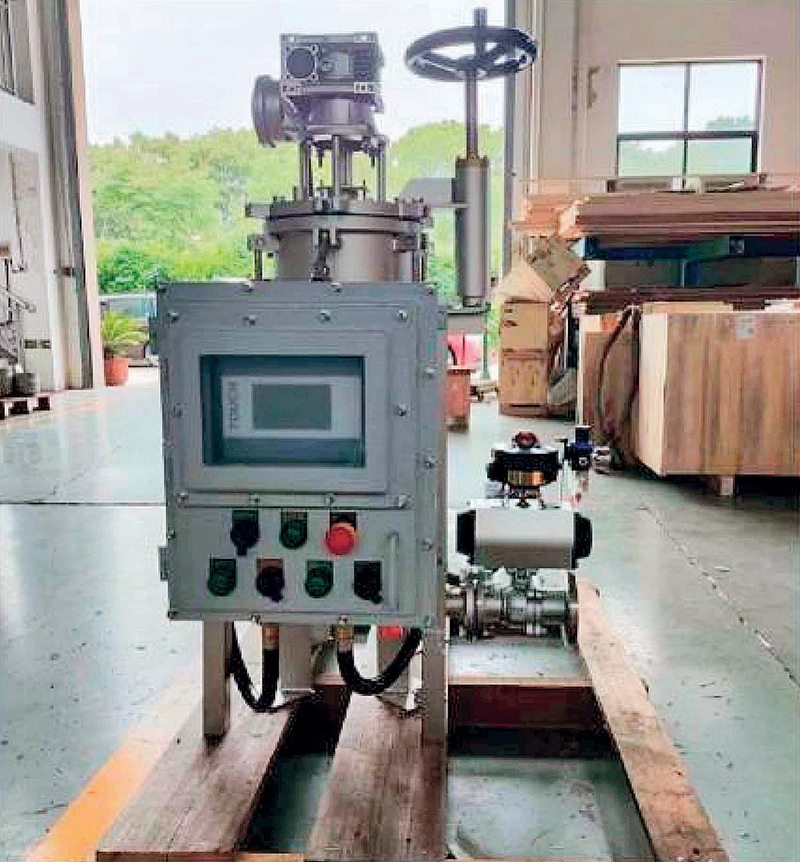
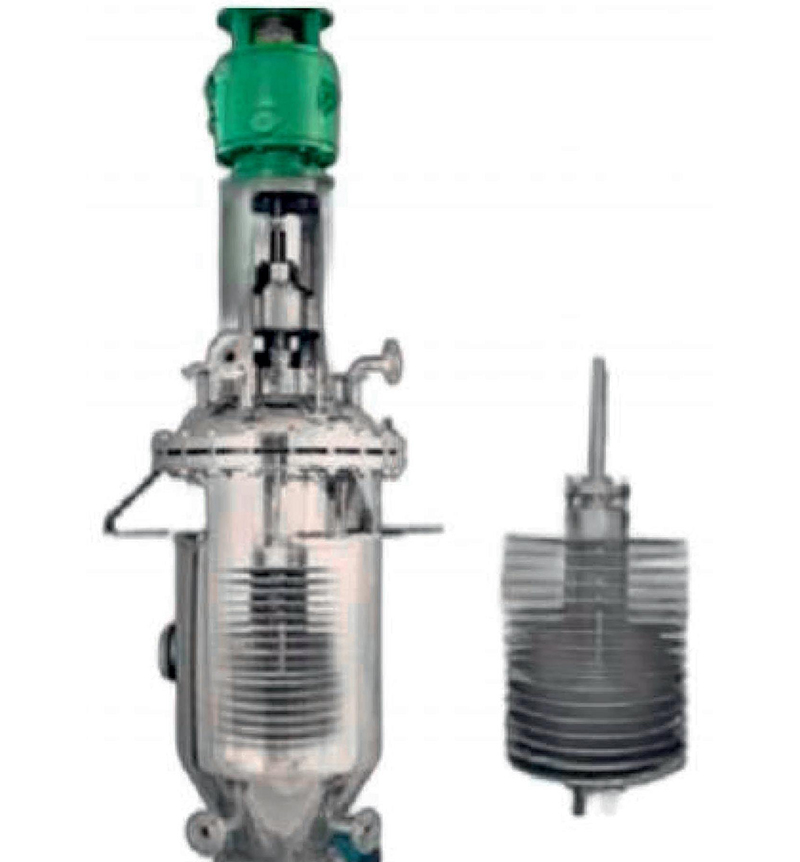
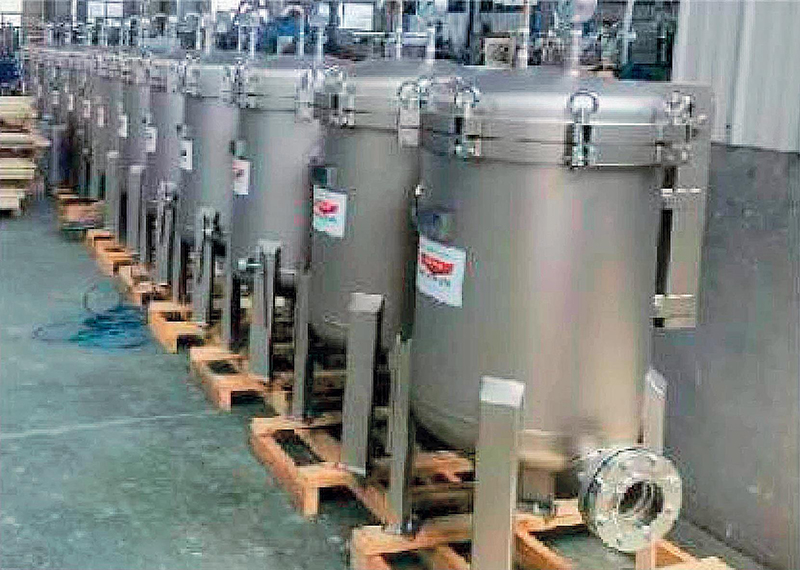
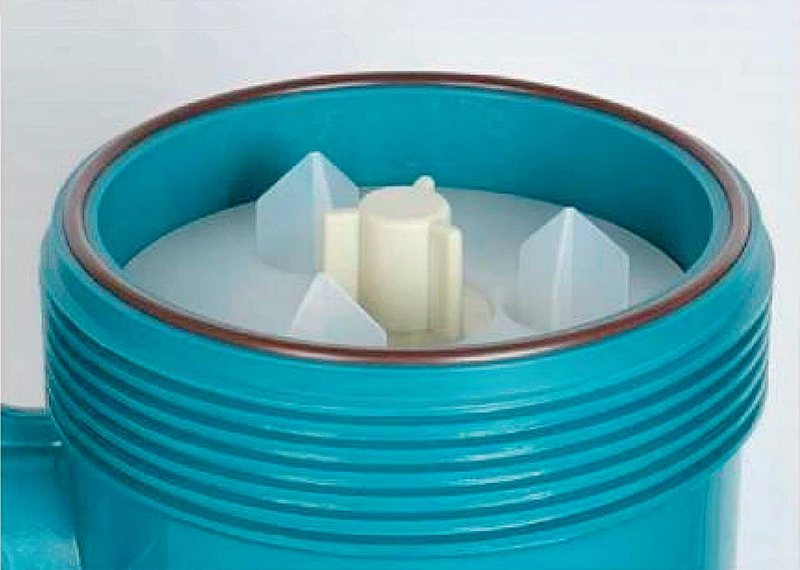

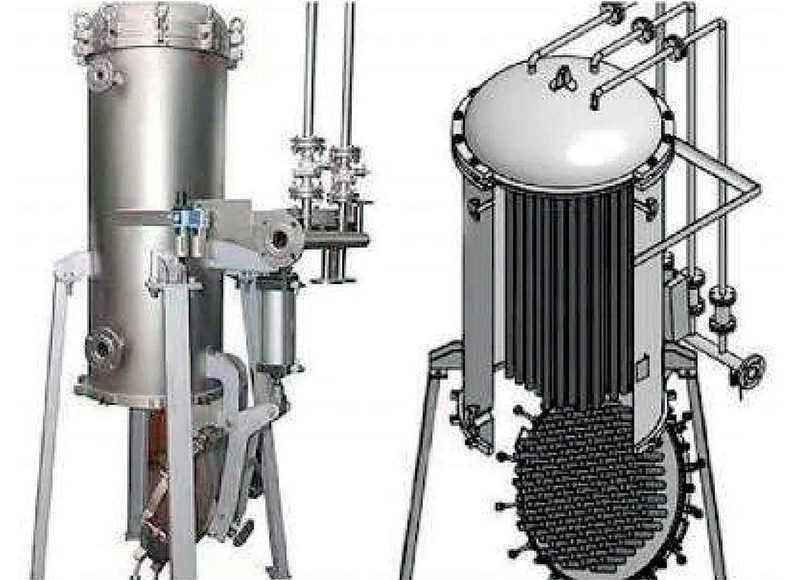




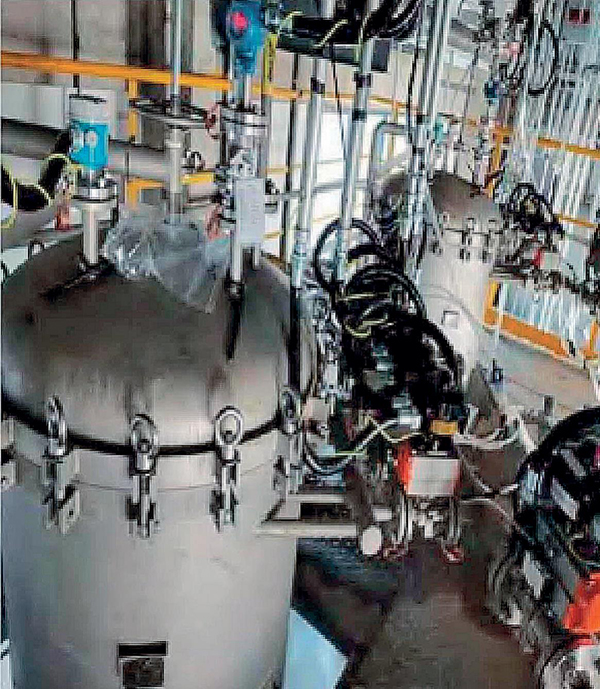
Application examples Of Agglomerator
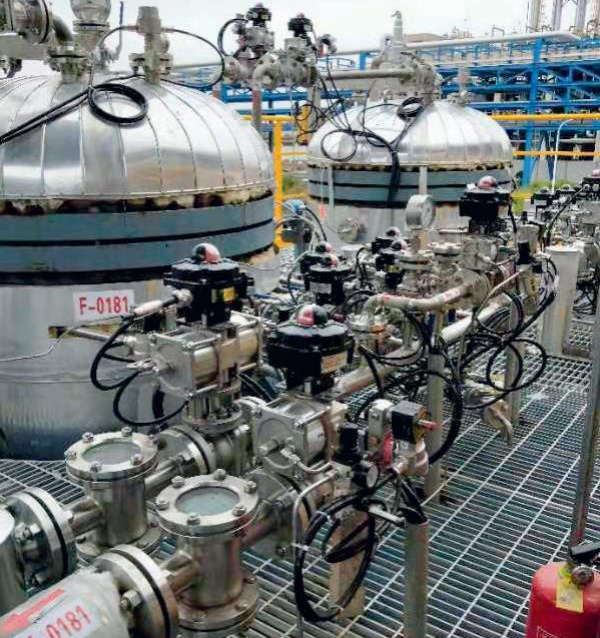
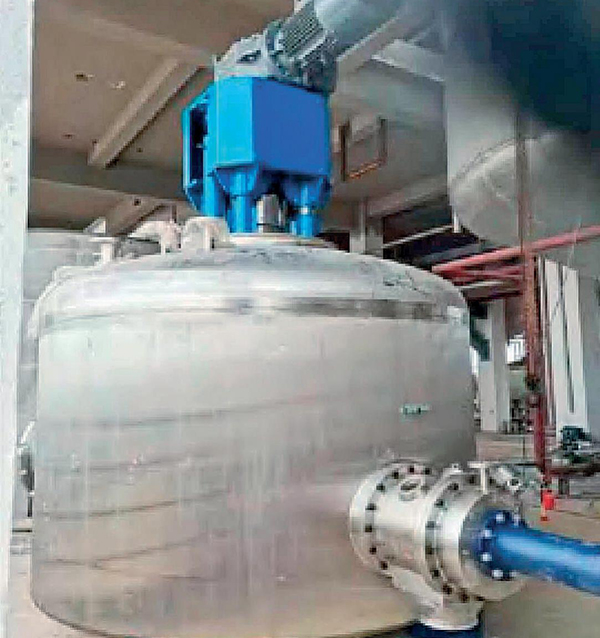
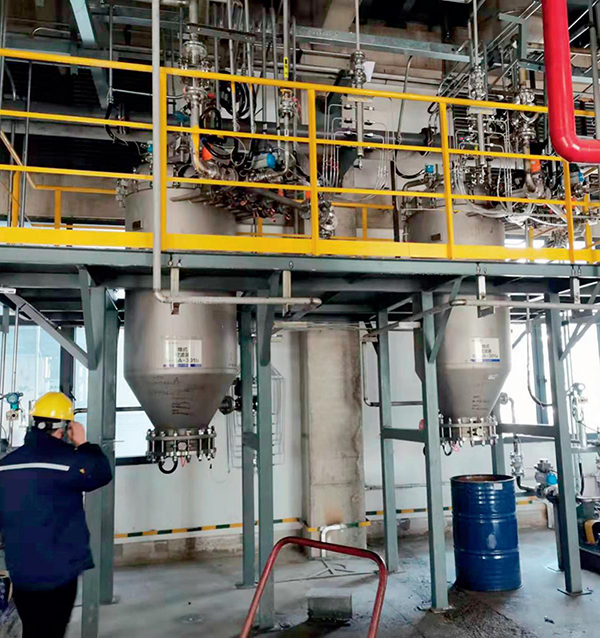
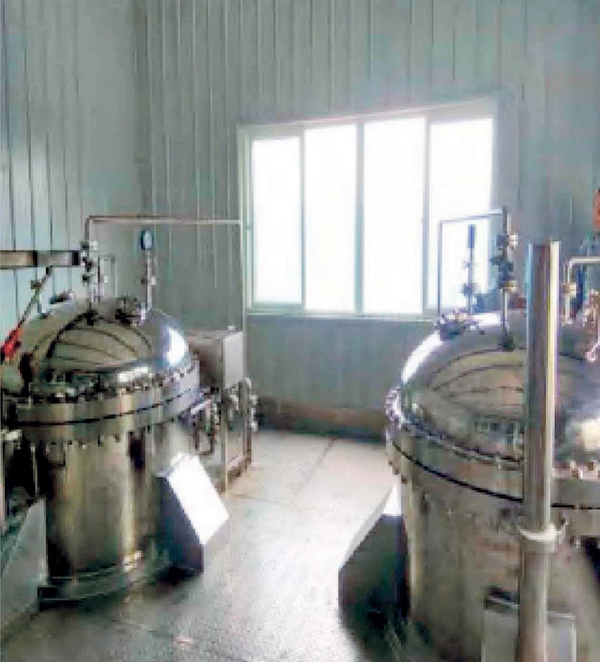
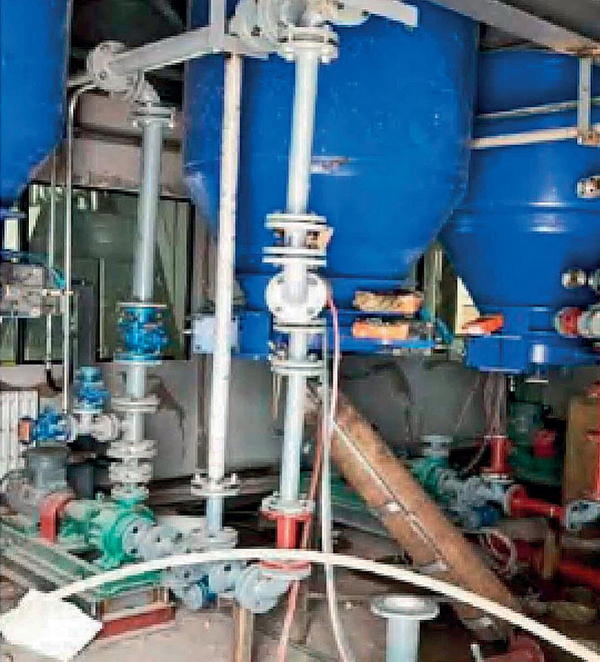
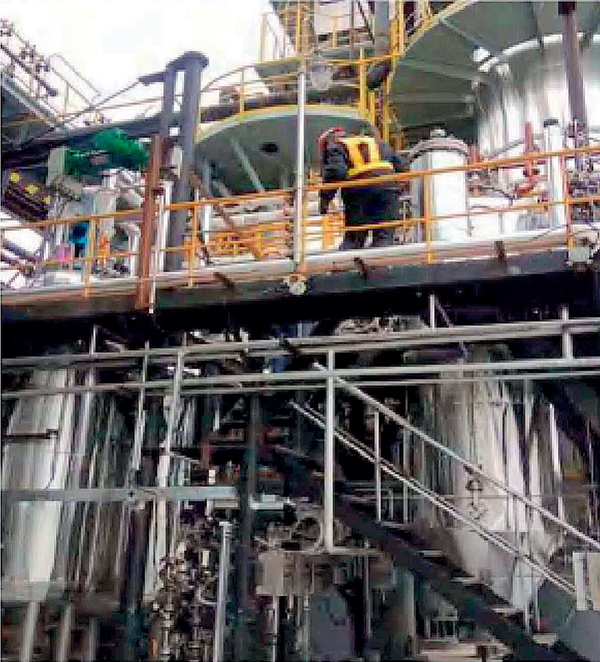
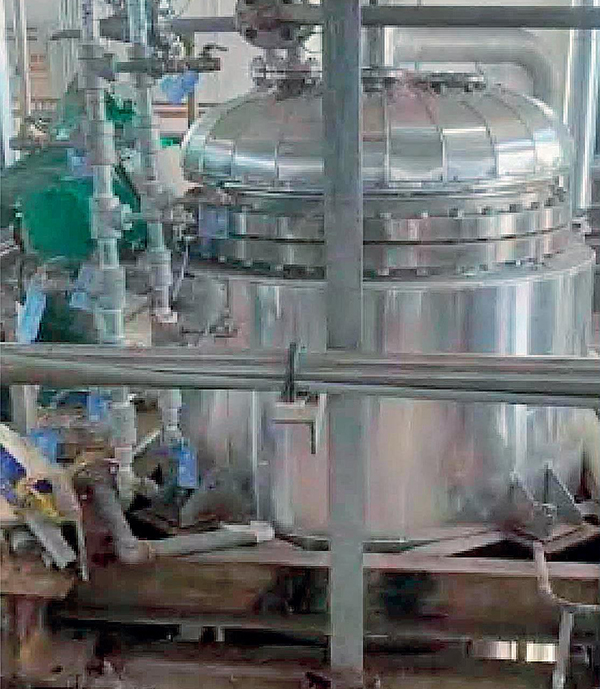
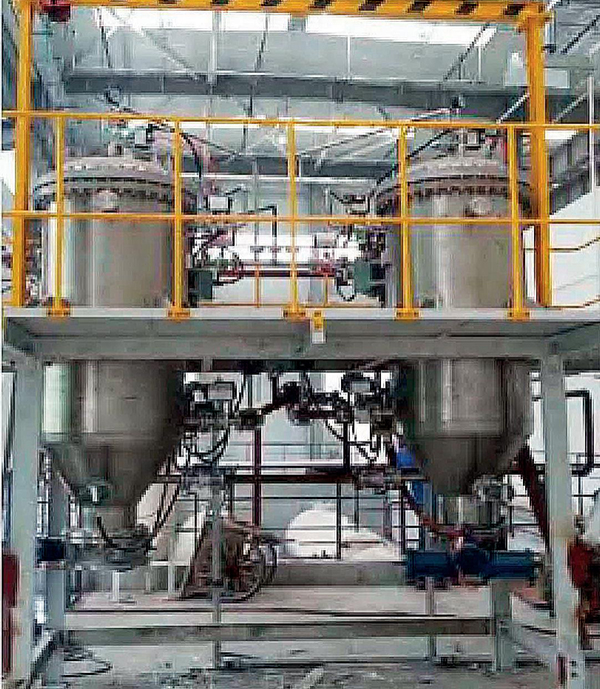
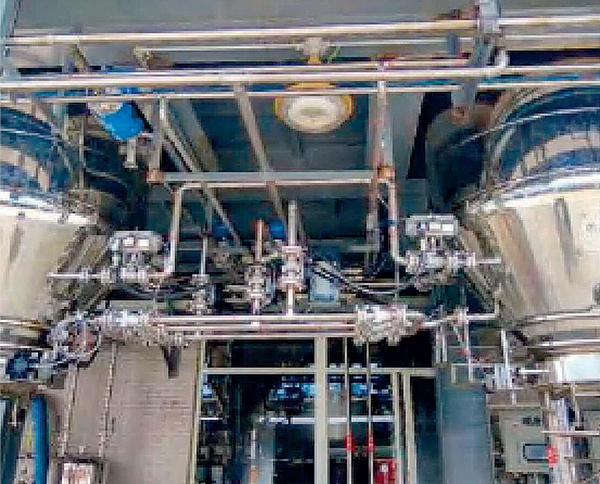
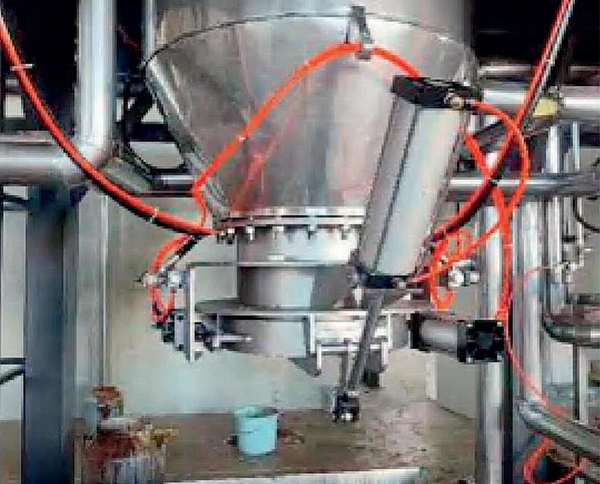
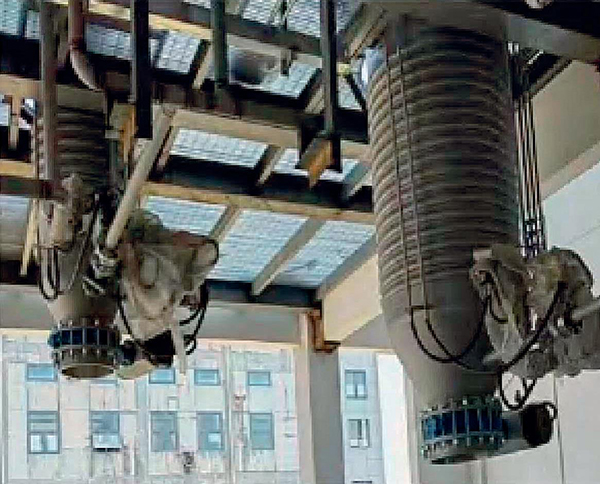











Hot Products
SEARCH
Products
- Filter Cloth
- Filter Cartridge
- PP Folding Filter Cartridge
- PES Folding Filter Cartridge
- PTFE Hydrophilic Folding Filter Cartridge
- PTFE Hydrophobic Folding Filter Cartridge
- Nylon Folding Filter Cartridge
- PALL Large Folding Filter Cartridge
- 3M Large Folding Filter Cartridge
- PARKER High Folding Filter Cartridge
- Large Flow Bag Filter Cartridge
- Melt-Blown Filter Cartridge
- Wire Wound Filter Cartridge
- Activated Carbon Filter Cartridge
- Filtration Apparatus
Get a Quote
We will provide you with the best quality products and the best price according to your order.







